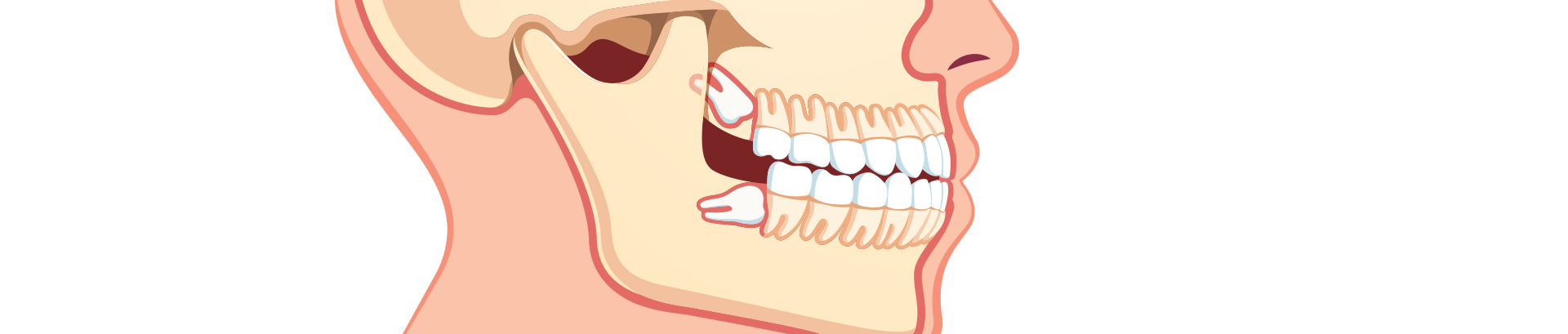
Wisdom teeth develop in the back corners of the upper and lower dental arches. Impaction happens when there is not enough space for the wisdom teeth to develop and they begin to grow at different angles (wisdom teeth impaction).
Some individuals may not recognise their wisdom teeth are not developing normally or healthily. Attending a regular dental check-up to monitor wisdom tooth growth can help to identify the early signs of wisdom teeth impaction for appropriate treatment.
In the majority of cases, people are aged between 18 and 25 and the wisdom teeth become impacted due to dietary and evolutionary changes. It is increasingly common for individuals to need treatment for impacted teeth. If left untreated, wisdom tooth infection or jaw disorders may develop and require emergency dental care.
Using diagnostic tests enables dental professionals to assess wisdom teeth condition and recommend treatments if impaction is present. The type and severity of dental impaction may differ and require alternate treatments.
Types of Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom teeth that develop abnormally may grow into neighbouring teeth or the gum tissue. For this reason, wisdom teeth impaction is usually categorised as:
- Vertical – grows down and locks the neighbouring tooth causing misalignment
- Horizontal – grows at 180 degrees to the tooth in front of it causing misalignment
- Mesial – grows at 45 degrees to the tooth in front of it causing misalignment
- Distal – grows backwards into the rear jaw bone causing jaw disorders
Although mesial impaction occurs most often any of the above impactions may range from mild to severe and lead to malocclusion and jaw disorders. Individuals may experience jaw pain and be at higher risk of infection. Treating wisdom teeth impactions early relieves painful symptoms and reduces the need for more extensive orthodontic treatment.
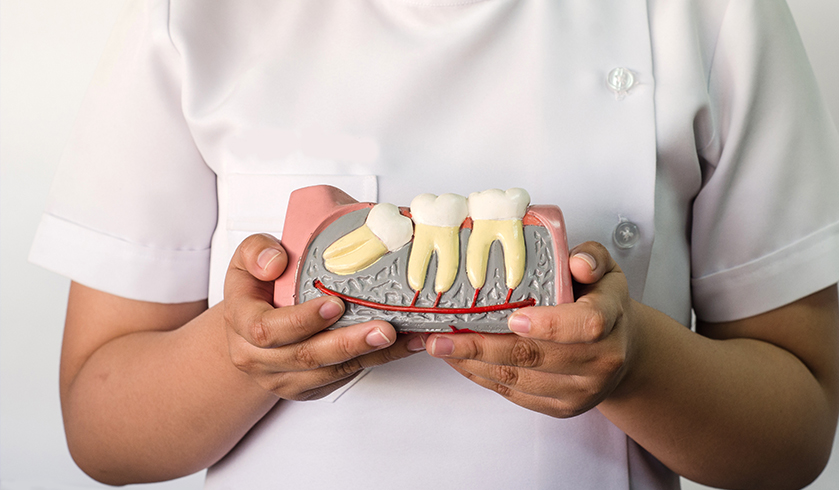
Impacted wisdom teeth, particularly where infection is present, are often extracted to prevent dental irregularities, teeth misalignment and orthodontic conditions. The wisdom teeth pockets are vulnerable to infection and so wisdom teeth extraction is often provided to prevent the spread of infection into root canals.
The irregular manner in which wisdom teeth impaction develops and the location of the wisdom teeth at the back of the jaw may make it harder to access the teeth for proper cleaning. Wisdom tooth decay is a risk because trapped food attracts plaque and bacteria, causing dental infection.
Having regular dental check-ups, professional teeth cleaning and scaling, as well as addressing dental concerns early, helps to reduce the effects of wisdom teeth impaction and treat early signs of decay and infection.
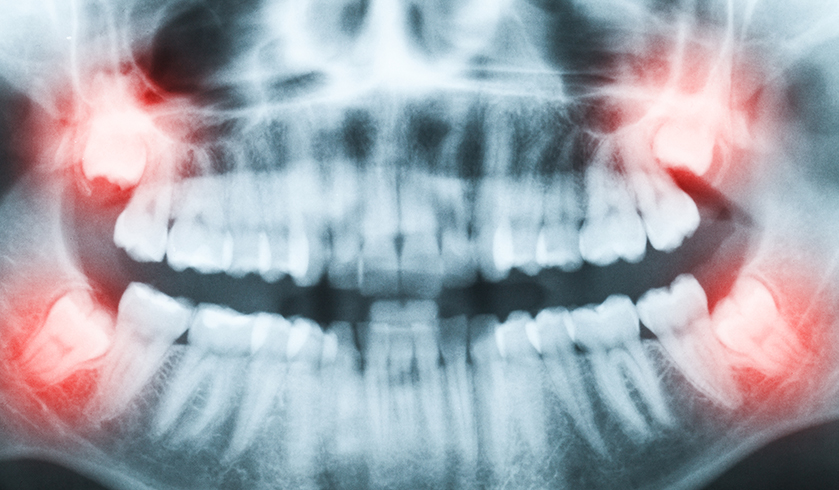
Treatments vary as to whether the impacted teeth have grown into gum tissue, neighbouring teeth or bone. Procedures may involve gum slicing, orthodontic care, oral surgery or tooth extraction. The only way to determine the extent of impaction and relevant treatment is by having the wisdom teeth assessed. X-rays or CT imaging may be used to identify wisdom teeth growth and impaction type for appropriate treatment.
Individuals are fully involved in their care plans and course of treatment. Where surgery is required a consultation will be provided to discuss the operation. Wisdom tooth surgery or extraction may require a general anaesthetic for pain-free treatment. Individuals may be advised not to eat or drink for 24 hours prior to the operation and will be give preparation guidelines.
The individual is either admitted within the clinic or a hospital out-patient unit for the impacted wisdom teeth operation. Once the individual is provided with general anaesthesia for wisdom teeth impaction surgery they go into a deep sleep.
The procedures may involve the slicing and lifting of gum tissue to expose the wisdom tooth for extraction. In some cases, the bone is removed in pieces. Once extracted the gum tissue flap is stitched back into position with dissolving sutures.
Once the anaesthesia wears off after the operation the individual may experience temporary gum swelling and discomfort, which is easily relieved with painkillers recommended by the oral surgeon or dentist. Patients are provided with post-operative care guidelines and discharged when they are deemed safe and ready to return home.
Patients will need to be accompanied home after the operation and are advised against driving or the use of machinery.
As part of the patient’s care plan the dentist or oral surgeon will discuss relevant risks, benefits and costs of oral surgery for impacted wisdom teeth. Risks and complications are inherent in all forms of surgery, such as infection and bleeding.
After wisdom teeth surgery the individual may experience some side-effects, such as bleeding from the wisdom tooth socket, but this is usually relieved by biting down on cotton wool to absorb the blood. Bruising and swelling of the cheeks and jaw is not uncommon, particularly when multiple wisdom teeth have been removed or where there is severe impaction.
Patients are advised to have a liquid and soft food diet for at least 24 hours after the surgery. Antibiotics and painkillers may be prescribed to reduce the risk of infection and relieve discomfort. An ice-pack may also be provided to decrease effects of swelling, bruising and soreness.
The risks include damage to oral structures, nerve damage, numbness, wisdom tooth remains, infection and unforeseen complications. Side-effects are mostly temporary. Sensations of short-term mouth, tongue or lip numbness should subside after a few days. However, certain complications may continue and the oral surgeon or wisdom teeth dentist should be notified for appropriate care.
Dry socket is another risk if a blood clot does not develop properly and seal the wisdom tooth socket where extraction took place. The socket can then become inflamed and painful, requiring a dental dressing to aid healing and sooth the pain.
High temperature and fever sometimes develop if infection sets in. A course of antibiotics can be provided to clear up the infection. Rarer are jaw alignment or sinus complications, but these are all risks that will be discussed with the patient prior to treatment so they know what to expect.
Patients are encouraged to continue their oral hygiene routine after surgery, with particular care to only rinse the treated wisdom teeth site. Once the area is healed and sutures dissolved within a few weeks, patients can gradually return to normal cleaning of the site.
Oral hygiene involves cleaning all oral structures, including the gums, palate, tongue and teeth. All people need to brush their teeth according to proper technique after meals and before sleep on a daily basis. Daily flossing to remove food debris between teeth is also needed to prevent plaque build-up. Using fluoride toothpaste and mouth rinse helps to prevent tooth decay, infection and gum disease.
Proper oral hygiene practice is a preventative measure to keep bacteria at bay and the teeth and gums healthy.
Contact us by phone or email and a member of our friendly team can make an appointment to assess your oral health and provide treatment recommendations where necessary.